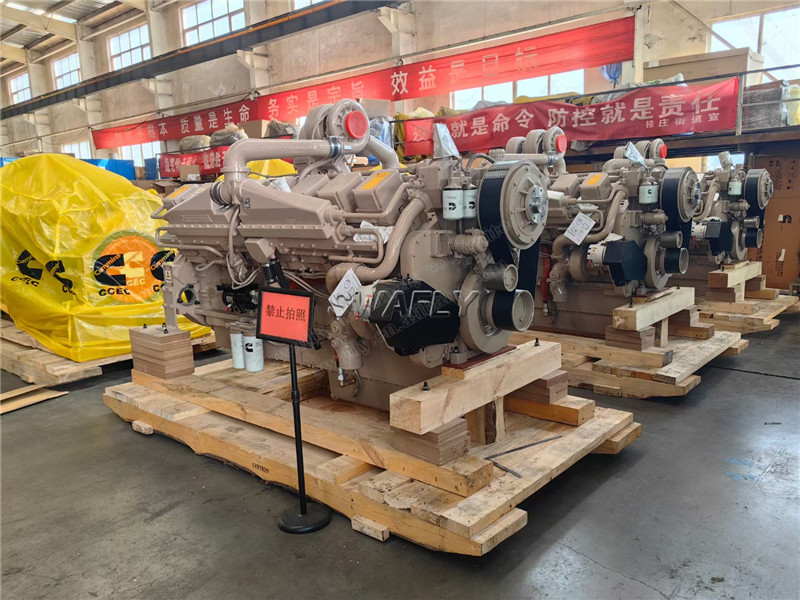
What Is a Diesel Engine, And What Are the Types and Components of a Diesel Engine?
Time:
2024-02-23
2-Stroke Diesel Engine: The 2-stroke engine completes a full cycle in just two strokes. Initially, air enters the cylinder, displacing the existing air. Subsequently, the compression process takes place. As the piston approaches the top of the cylinder, diesel fuel is introduced, leading to the generation of chemical energy.
Advanced diesel engines drive many of the world's essential industries. Boats, barges, and semis transport the majority of everyday consumer goods. Agricultural machinery guarantees the production of the food and natural resources necessary for our needs. Construction equipment plays a crucial role in powering and maintaining our infrastructure.
But what precisely is a diesel engine? How does it operate? And what are the key components and characteristics of a diesel engine? Explore the fundamentals in this blog post.
WHAT IS A DIESEL ENGINE?
At its core, a diesel engine belongs to the category of internal combustion engines. Internal combustion engines are heat engines that generate power through the combustion of fuel and an oxidizer. In the case of a diesel engine, mechanical energy is produced by compressing air and diesel fuel.
But how exactly does a diesel engine operate? The process is relatively straightforward. Initially, air is drawn into the cylinders and subsequently compressed by pistons, typically between 14 and 25 times, generating heat. Once the air is compressed, diesel fuel is sprayed into the cylinders by fuel injectors. The introduction of diesel fuel into the heated air initiates ignition, resulting in the production of chemical energy. The combustion forces the piston out of the cylinder, converting the chemical energy into mechanical energy. This cycle repeats hundreds to thousands of times per minute, generating sufficient energy to propel a vehicle.
WHAT ARE THE TWO TYPES OF DIESEL ENGINES?
Diesel engines can be classified in various ways, commonly based on their power output (small, medium, and large). Another distinguishing factor is the number of strokes required to complete an engine cycle, resulting in two main types: 2-stroke engines and 4-stroke engines. As the names suggest, 2-stroke engines complete the cycle in two strokes, while 4-stroke engines do so in four. Let's delve into a closer examination of each type of diesel engine:
2-Stroke Diesel Engine:
The 2-stroke engine completes a full cycle in just two strokes. Initially, air enters the cylinder, displacing the existing air. Subsequently, the compression process takes place. As the piston approaches the top of the cylinder, diesel fuel is introduced, leading to the generation of chemical energy. This energy propels the piston downward, transferring mechanical energy to the wheels.
Generally, 2-stroke diesel engines are lighter and more compact than their 4-stroke counterparts. However, the reliance on only two strokes makes them more prone to wear and tear, contributing to the comparatively lower prevalence of 2-stroke engines.
4-Stroke Diesel Engine:
In a 4-stroke engine, the pistons undergo four distinct movements—two upward and two downward strokes. In addition to the compression and exhaust strokes, as detailed previously, the pistons also execute return strokes. The process commences by drawing air into the cylinder as the piston descends. As the piston ascends, the air undergoes compression. Upon reaching the top of the cylinder, fuel injection initiates the ignition process. The ignited fuel forces the piston downward, releasing mechanical energy to drive the wheels. Finally, the piston ascends again to expel the burned gases.
4-stroke engines are the most prevalent type, commonly found in diesel trucks and automobiles.
WHAT ARE THE MAIN PARTS OF A DIESEL ENGINE?
Diesel engines are made up of dozens of parts. However, the engine parts list below provides information about nine of the most vital components.
Block - Serving as the foundational component of the modern diesel engine, the block contains all the essential parts for the basic internal combustion process. Within the block, there is an open space for each cylinder, where combustion takes place.
Pistons - Positioned at the bottom of the combustion chamber, pistons move up and down within the cylinder during engine operation. This motion generates the compression of air, a crucial step leading to combustion.
Cylinder Head - Closing the top of the open space within the block to encase the chamber where combustion occurs, the cylinder head can either be a singular unit covering all cylinders or multiple units that span specific sections.
Valves - With the cylinder sealed by the piston at the bottom and the cylinder head at the top, a mechanism is necessary to facilitate the influx of fresh air and the expulsion of residual gases. This role is fulfilled by valves, typically two for intake and two for exhaust for each cylinder.
Fuel Injectors - Now, a mechanism is required to introduce fuel into the cylinder, providing substance for combustion. These components play a sophisticated role in the process, employing precise patterns and highly controlled timing to spray fuel.
Camshaft - Instead of relying on an electrical system to regulate valve openings and fuel injection, most engines employ a mechanical process. The revolutions of the camshaft dictate the timing of these events, facilitated by lobes on the shaft that set them into motion.
Connecting Rods - These components attach to a piston at the bottom arm and transmit the force generated during combustion to the crankshaft.
Crankshaft - Responsible for converting the linear motion of combustion (the up-and-down phase of the combustion process) into rotational motion, the crankshaft plays a crucial role in the overall functioning of the engine.
More News